The Significance of Authentication Security: Lessons from the Aladin Hacking Incident
In May 2023, a 16-year-old teenager emerged as the mastermind behind a cyberattack on the prominent online and offline used bookstore, Aladin, resulting in the theft of approximately 1.4 million e-books. A second-year high school student successfully infiltrated Aladin’s defenses and extorted around 80 million won in bitcoin and cash from the company.
The Cause of a Hacking Incident

E-book service companies, such as Aladin, encrypt their content with Digital Copyright Management (DRM) to ensure that only buyers can access it. The decryption keys, such as passwords, necessary to unlock this content, are typically stored on a server.
In most cases, e-book service companies utilize a cache server called CDN (Content Delivery Network) to store encrypted e-books. However, these CDN servers often prioritize availability over security, and their authentication procedures and policies are frequently lacking.
For companies offering e-books and video streaming content through CDN servers, maintaining uninterrupted internet services is crucial. Balancing security with service load is a challenge, as increased security measures can lead to customer dissatisfaction.

In a recent incident, Mr. A exploited security vulnerabilities within a victim company, driven by his usual interest in breaking digital copyright management technology (DRM). Mr. A managed to hack into a server that was exposed to the outside world, extracting the decryption key and gaining unauthorized access to e-books.
Following this incident, the e-book industry is urging for enhanced authentication and external access procedures to safeguard electronic document storage.
The Importance of the Authentication Process
Authentication is a crucial aspect of e-book usage, and device authentication holds significant importance. Nonetheless, in numerous cases, e-book terminal solutions do not incorporate a secondary authentication process, including biometric authentication. Furthermore, even when a secondary authentication method is available, it might not be utilized during e-book purchases or access.
To prevent the recurrence of such incidents, it has been emphasized that the introduction of a security solution capable of ensuring stability is necessary. This could involve reinforcing the authentication process with step-by-step multi-authentication when using e-books and implementing security modules on CDN servers. In response, e-book service companies have stated their intention to adopt these measures gradually due to the substantial cost and effort required to enhance the security system.

The hacking incident revealed the vulnerability of depending solely on user logins as a security measure, emphasizing the necessity for a more vigilant approach. As a result, the content service industry is increasingly advocating for the adoption of a Zero Trust security model.
Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust has evolved into a global trend across various sectors, including content services like e-books, as well as IT, telecommunications, finance, healthcare, and public institutions.
Zero Trust is a security concept that prioritizes safeguarding critical company data by consistently verifying all users and devices seeking access to the corporate network, operating on the principle of “Trust nothing and always verify.”
📌 Core principles of Zero Trust
https://www.cloudbric.com/3-core-principles-of-zero-trust/
To prepare for cyberattacks like the Aladin hack mentioned earlier, it is crucial to implement Zero Trust as a means of fortifying the authentication and external access processes when dealing with sensitive enterprise data.
Conventional ID and password-based authentication methods frequently require the inclusion of a multi-factor authentication (MFA) process due to the potential vulnerability of exposure, which may involve methods like email-based authentication codes or one-time password (OTP) codes. Moreover, by enforcing differentiated and granular access control for authorized users based on their respective roles and privileges, the protection of sensitive data is bolstered, and the risk of data leaks is significantly reduced.
Zero Trust places a strong emphasis on establishing robust authentication policies and employing authentication techniques for both users and devices to secure access to enterprise systems. Even for individuals who already have access, Zero Trust offers a higher level of security by continuously verifying user credentials before granting access to key data.
Implementing ZTNA Security Solutions
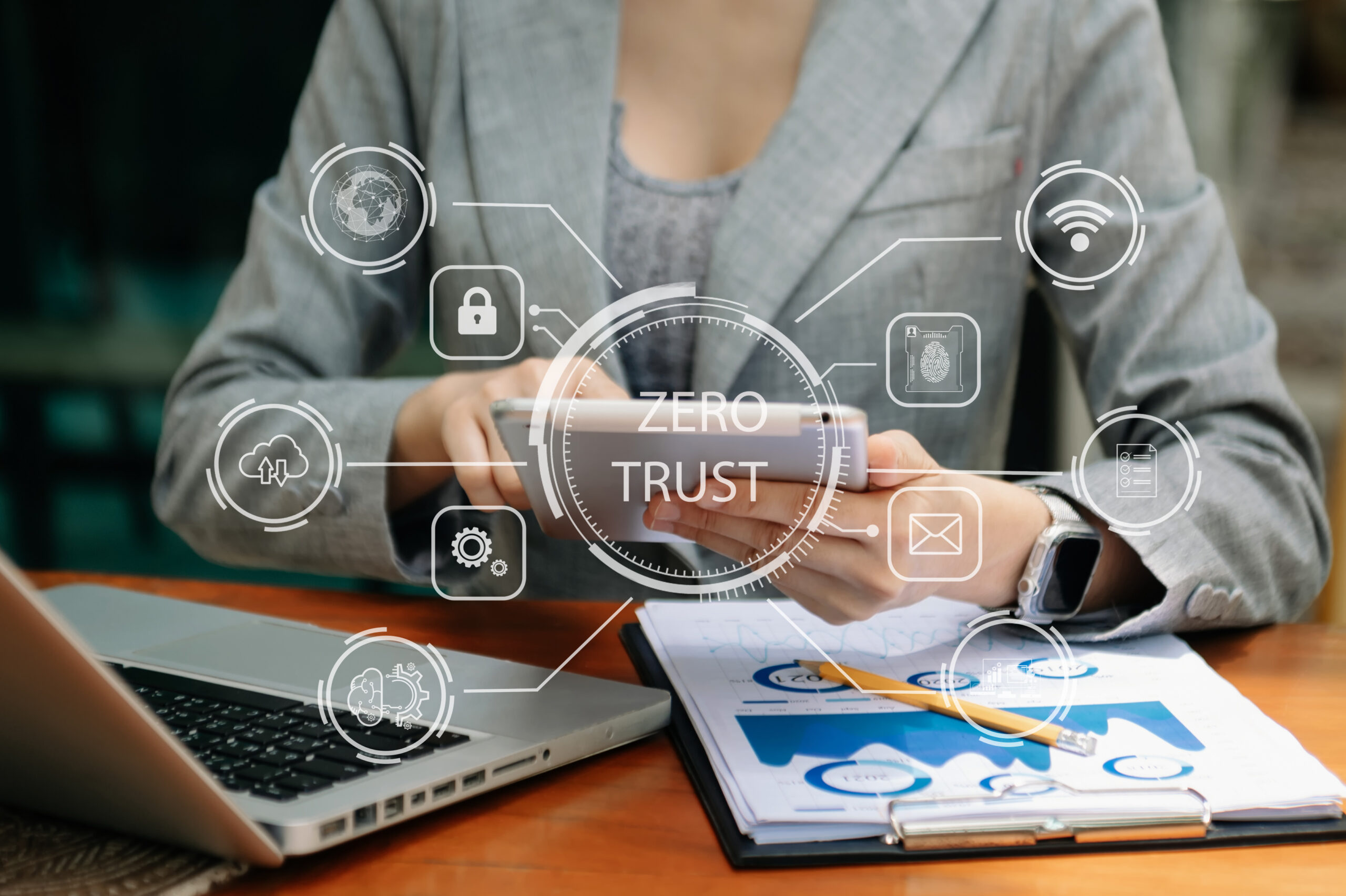

While many security experts stress the significance of adopting zero-trust, there are various opinions suggesting that implementing zero trust technology can be challenging for companies. Implementation of Cloudbric PAS (Private Access Solution), a SaaS-based ZTNA(zero trust network access) security solution, allows companies to enhance authentication processes and address security concerns associated with external access.
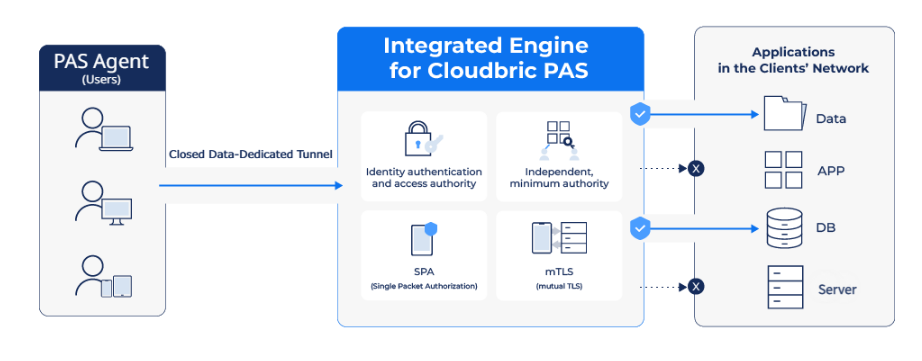
Cloudbric PAS (Private Access Solution) incorporates a 2FA(2-factor authentication) that verifies both user and device identities while providing access control based on the organization’s own security policies and micro-segmentation. Furthermore, it employs virtual IP addresses to access the enterprise’s network, thereby safeguarding the internal network by not disclosing the actual server connection information.
📌 Learn more about Cloudbric PAS
As demonstrated by the Aladin case, when a company becomes a target of a hacking attack, the potential for significant damage is evident. This may involve the exposure of sensitive data or the encryption of data with ransom demands.
In response to such incidents, it becomes crucial to strengthen your enterprise network’s security. Implement zero-trust security solutions like Cloudbric PAS (Private Access Solution) to enhance both the authentication process and external access protocols, thereby securing sensitive enterprise networks.