Hackers are always finding new ways to transform traditional attacks to make a more effective and powerful cyberattack. Recently, an attack called Ransom DDoS or RDDoS attack has been targeting the financial sector. In this blog, we will discuss what an RDDoS attack is and how it threatens users.
First threaten, then attack
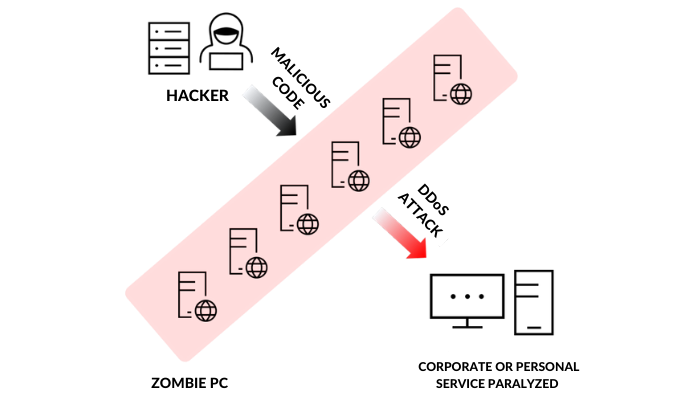
Ransom DDoS has a similar name to a cyberattack known as ransomware. Ransomware is a type of cyberattack that uses a combination of a ransom and software that encrypts data and demands money such as Bitcoin for the return of data, system access, and so on; the same goes with ransom DDoS.This name was given because hackers in real-life demand payment before proceeding with a DDoS attack. If they don’t receive the Bitcoin they want, hackers will proceed with the attack. So what is exactly a DDoS attack? A DDoS attack is a cyberattack where hackers send out massive traffic at a particular site using multiple computers to paralyze the server. So when a company server goes down due to a DDoS attack they will not only experience loss of money but also the damage of brand image, and this is what hackers are after.
 Catch victims off guard
Catch victims off guard
During a major holiday in Korea, a number of attempts directed at financial companies with Ransom DDoS were seen. Hana Bank, Woori Bank, Industrial Bank of Korea, and Busan bank all received a threatening email demanding millions of won in Bitcoin. In August, Shinhan Bank, Kakao Bank, and K-Bank were attacked by a DDoS after receiving those threatening emails. Fortunately, in the financial sector, even if a DDoS attack takes place there is no major damage, related to direct financial loss. However, attention should be paid to the possible cyber accidents that can occur during the COVID-19 pandemic with the increased use of telecommunicating forms in companies. When a hacker continues to fail at launching a Ransom DDoS attack, there is a possibility that the hacker will make a stronger pattern of attack and keep attacking your server. With more malicious traffic entering the server compared to the previous DDoS attack, it will become more difficult to respond to it.
How to stop a Ransom DDoS
 The DDoS attack is the key to a Ransom DDoS. So if your company can prevent a DDoS attack, then you can eventually also prevent the Ransom DDoS attack without having to pay up. In the past 5 years, DDoS attacks account for about 62% in the financial industry. So how should we stop it? DDoS attack generates large traffic simultaneously through bots, so it is necessary for you to distinguish if a traffic is healthy (i.e. legitimate) or not. Based on your data on normal traffic patterns and sizes, you will be able to quickly identify and respond to a DDoS attack. Many cyberattacks, especially DDoS attacks, occur at the application layer (Layer 7), which means that companies that want to protect their sensitive data are required to adopt a web application firewall that can quickly identify and respond to all types of cyber-attacks. One example of a security service is Cloudbric’s Web Application Firewall. It is a cloud-based security solution. With just simply changing your DNS information your company’s website will be effectively protected from DDoS attacks. Furthermore, Cloudbric’s DDoS Advanced Solution is a more specialized security solution that defends DDoS and it protects your website against 20 Tbps DDoS attacks. With no DDoS attacks over 2Tbps worldwide so far, Cloudbric’s DDoS Advanced Solutions can effectively defend against rapidly escalating DDoS attacks, enabling users to run reliable websites.
The DDoS attack is the key to a Ransom DDoS. So if your company can prevent a DDoS attack, then you can eventually also prevent the Ransom DDoS attack without having to pay up. In the past 5 years, DDoS attacks account for about 62% in the financial industry. So how should we stop it? DDoS attack generates large traffic simultaneously through bots, so it is necessary for you to distinguish if a traffic is healthy (i.e. legitimate) or not. Based on your data on normal traffic patterns and sizes, you will be able to quickly identify and respond to a DDoS attack. Many cyberattacks, especially DDoS attacks, occur at the application layer (Layer 7), which means that companies that want to protect their sensitive data are required to adopt a web application firewall that can quickly identify and respond to all types of cyber-attacks. One example of a security service is Cloudbric’s Web Application Firewall. It is a cloud-based security solution. With just simply changing your DNS information your company’s website will be effectively protected from DDoS attacks. Furthermore, Cloudbric’s DDoS Advanced Solution is a more specialized security solution that defends DDoS and it protects your website against 20 Tbps DDoS attacks. With no DDoS attacks over 2Tbps worldwide so far, Cloudbric’s DDoS Advanced Solutions can effectively defend against rapidly escalating DDoS attacks, enabling users to run reliable websites.
Conclusion
If you do not like the fact that hackers are demanding payment for the stolen data which was yours in the first place, be wary of Ransom DDoS. With proper security protection, it is not that difficult to prevent those attacks. But don’t underestimate that hackers are going to attack your server with the same pattern each time. Because hackers somehow find ways to develop a much more harmful attack. Companies need to prepare for effective ways to respond to these attacks by establishing a security strategy and by adopting a solution that can prevent a variety of attack patterns.