Importance of the Zero Trust technology and Agent-based Zero trust network solution, Cloudbric PAS (Private Access Solution)
Zero trust security model caused by the expansion of cloud environments
The rise of remote work has led to increased flexibility in terms of working hours, methods, and locations, freeing employees from the constraints of traditional office settings. As a result, companies have shifted their environments to the cloud to enable access to their applications from anywhere at any time. However, the use of a variety of programs across multiple networks has made management and security more complicated.
This old security model of “outside is dangerous, inside is safe” is no longer effective in today’s remote working environment. The risk of an outdated security model that assumes that all processes within the enterprise network are completely reliable since users and applications coexist both inside and outside the enterprise has increased.
As a result, the concept of Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) was introduced in 2010 and gained popularity as a method to increase corporate security and reduce the complexity and risks associated with traditional security strategies.
The concept of Zero Trust (ZT) applied to zero trust network access is a security model proposed in 2010 by Forrester Research analyst John Kindervag, which is an approach to the method of ‘Never trust, always verify. It is a security model designed to ensure that no user or device can connect to a network until their account and permissions have been verified. This verification process is required for every connection, regardless of whether there is an existing or frequent network connection history.
Basic principles of Zero trust

The Zero Trust concept is based on several key principles that experts agree are critical to its effectiveness. These principles are:
- Continuous Monitoring and Verification: The Zero Trust model assumes that attackers could be both inside and outside the network, so it continually verifies user identity and permissions. It checks for verification every time a user attempts to access the network, regardless of their history.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a method where a user presents two or more forms of evidence to verify their identity. In other words, in addition to knowledge-based authentication factors (such as passwords that only the user knows), ownership-based authentication factors (user-owned element-specific information), or attribute-based authentication factors (user-specific physical characteristics) are used to enhance security.
- Device Access Control: With the rise of remote work and the use of various devices to access the network, monitors the number of devices attempting to access the network and evaluates them for authentication and corruption to minimize network attacks.
- Minimize Access Authority: Providing users with as much access as they need requires careful user authority management. Minimizing user exposure to sensitive parts of the organizational network is an effective way to prevent unauthorized access.
- Micro segmentation: Micro segmentation involves dividing security boundaries into small areas with established access rights. This helps protect the expanded surface of network boundaries in cloud environments and minimizes the extent of damage in the event of a breach.
How to establish Zero Trust Network Access?
The first step in establishing zero-trust network access is to identify the most critical and valuable components of the enterprise network. This enables the prioritization of attention and resources to the areas that require the highest level of security. The next step is to examine user identities, application usage, and network connections in detail.
It is recommended to follow these three steps to establish a suitable zero trust strategy by considering user (authentication, minimum access policy, and verification), application (continuous authentication and monitoring), and infrastructure (IoT, supply chain cloud, etc.).
- Visualization: The access points and potential risks associated with all resources need to be understood.
- Mitigate: The threat should be identified or stopped to reduce the damage that has already occurred.
- Optimization: Extending protection across all aspects of the organization’s network and all resources within the network without compromising the user experience.
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) Solution of Cloudbric

A zero trust approach is required for every organization. Understanding how it works and applying it to your own network and technology can significantly improve the quality of cybersecurity. Cloudbric provides a zero trust network access (ZTNA) solution called Cloudbric PAS with high-quality cyber threat intelligence gathered from around the world based on the know-how of in-house security professionals.
Cloudbric PAS (Private Access Solution)
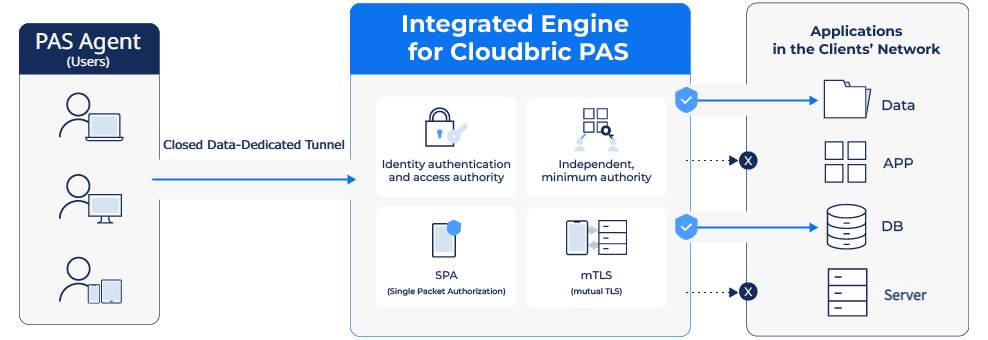
Cloudbric PAS is an Agent-based ‘ZTNA’ solution with Software Defined Perimeter (SDP) technology.
Only users authenticated by the agent can access encrypted private tunnels to connect to the enterprise network and use virtual IP to minimize attack surface by preventing external exposure of actual server connection information.
It provides a variety of identity verification (Two-factor authentication, device identity authentication), the organization’s own security policies, and micro segmentation-based access, all of which are easy and convenient to set up through the user console.
Learn more about Cloudbric PAS, an agent-based zero-trust network access solution on Cloudbric’s official website.