ZERO TRUST vs ZTNA vs SDP
 Since the emergence of COVID-19, there has been a significant transformation in the working environment of companies. Many organizations are shifting away from the conventional office-centric work setup and adopting hybrid work practices, including telecommuting, workstations, and base offices. These practices allow employees to work from different locations, breaking free from the constraints of a fixed physical workspace.However, these changes have also brought about a noticeable increase in security threats. As employees utilize various devices, including personal laptops, smartphones, and tablet PCs to access corporate networks, the importance of implementing robust security measures, such as Zero Trust, has become increasingly apparent.
Since the emergence of COVID-19, there has been a significant transformation in the working environment of companies. Many organizations are shifting away from the conventional office-centric work setup and adopting hybrid work practices, including telecommuting, workstations, and base offices. These practices allow employees to work from different locations, breaking free from the constraints of a fixed physical workspace.However, these changes have also brought about a noticeable increase in security threats. As employees utilize various devices, including personal laptops, smartphones, and tablet PCs to access corporate networks, the importance of implementing robust security measures, such as Zero Trust, has become increasingly apparent.
ZERO TRUST vs ZTNA vs SDP
As Zero Trust emerges as the next-generation security model for a secure hybrid work environment, technical terms like ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access) and SDP (Software Defined Perimeter) are frequently encountered. Zero Trust, ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access), and SDP (Software Defined Perimeter) are related security concepts, but they have distinct differences.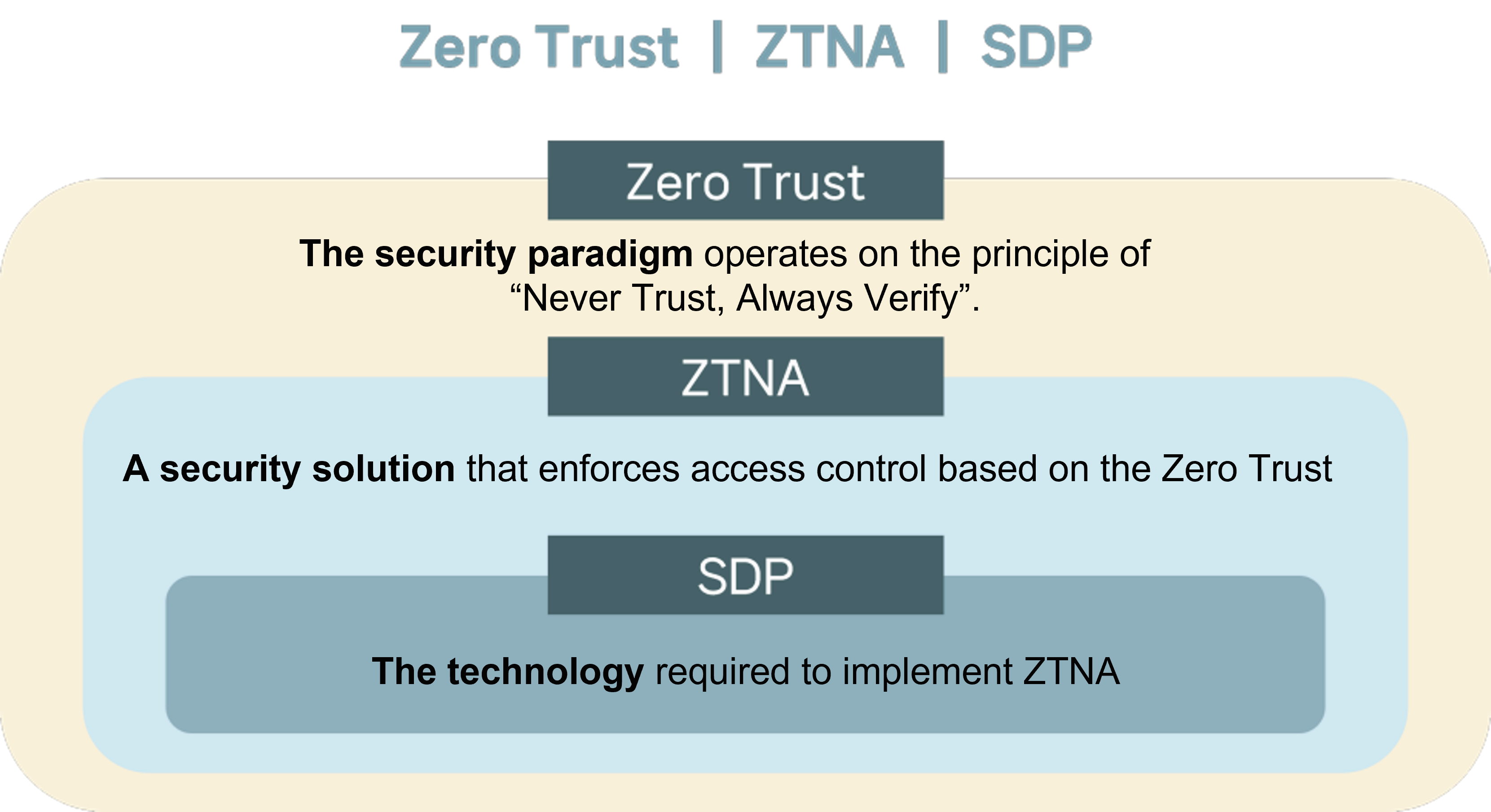 ① Zero TrustIn the past, many companies focused their security strategies on safeguarding internal systems against external threats. However, with the occurrence of several internal data leakage incidents, it has become evident that potential security risks exist both within and outside the system.Zero Trust is a security concept that prioritizes the protection of your company’s critical data by consistently verifying all users and devices connecting to your corporate network. Its fundamental principle is ‘Never Trust, Always Verify.’It is a robust security strategy that involves securing a corporate’s network by withholding access from anyone or any devices until an explicit need is identified.📌Learn more about Zero Trust
① Zero TrustIn the past, many companies focused their security strategies on safeguarding internal systems against external threats. However, with the occurrence of several internal data leakage incidents, it has become evident that potential security risks exist both within and outside the system.Zero Trust is a security concept that prioritizes the protection of your company’s critical data by consistently verifying all users and devices connecting to your corporate network. Its fundamental principle is ‘Never Trust, Always Verify.’It is a robust security strategy that involves securing a corporate’s network by withholding access from anyone or any devices until an explicit need is identified.📌Learn more about Zero Trust
② ZTNA, Zero Trust Network Access
ZTNA, also known as Zero Trust Network Access, is a form of access control security by implementing zero trust principles to safeguard data and applications when remote users access corporate resources.
With ZTNA, remote user access is automatically denied by default, creating a strong defense against potential security breaches. Access is granted only to trusted targets after successful identity authentication, following the security policies established by an enterprise.
ZTNA strengthens the protection of your on-premises system, ensuring that sensitive data remains secure from potential threats by blocking unknown approaches with a stance of not trusting all access.
③ SDP, Software Defined Perimeter
SDP is a next-generation access control framework that governs resource access based on identity. With robust authentication and highly restricted network access, SDP is one of the vital elements of ZTNA.
Unlike the traditional network security approach of “connect first, then authenticate,” SDP operates by granting connections solely based on the authentication results of identity. This prevents external intrusions and ensures secure application access exclusively for users with authenticated identities.
Zero Trust in Korea
 Zero Trust has gained global recognition as a new security model. However, its somewhat philosophical nature poses challenges in direct application to a corporation’s security system. Additionally, varying perspectives among countries have led to a lack of consensus and a shared understanding of Zero Trust principles.On July 9th, 2023, the Ministry of Science and ICT of South Korea unveiled “Zero Trust Guidelines 1.0” to strengthen security in domestic companies and institutions. These guidelines aim to enhance security measures, minimize trial and error, and facilitate the adoption of Zero Trust. It provides a comprehensive framework encompassing basic concepts, security fundamentals, core principles for the local IT landscape, reference model, and detailed procedures for planning and implementing Zero Trust deployments.
Zero Trust has gained global recognition as a new security model. However, its somewhat philosophical nature poses challenges in direct application to a corporation’s security system. Additionally, varying perspectives among countries have led to a lack of consensus and a shared understanding of Zero Trust principles.On July 9th, 2023, the Ministry of Science and ICT of South Korea unveiled “Zero Trust Guidelines 1.0” to strengthen security in domestic companies and institutions. These guidelines aim to enhance security measures, minimize trial and error, and facilitate the adoption of Zero Trust. It provides a comprehensive framework encompassing basic concepts, security fundamentals, core principles for the local IT landscape, reference model, and detailed procedures for planning and implementing Zero Trust deployments.
📌 Core principles of Zero Trust Security
✅ Enhanced Authentication
✅ Microsegmentation
✅ SDP (Software Defined Perimeter)
The Ministry of Science and ICT announced that they are conducting a project to accelerate the adoption of the Korean model of Zero Trust for the future and planning to leverage the “Zero Trust Guidelines 1.0” to enhance the understanding of Zero Trust.
In early 2023, Cloudbric introduced Cloudbric PAS, an agent-based Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) solution designed to establish zero-trust network environments within domestic enterprise settings.
Create a secure cloud environment by leveraging Cloudbric PAS, a robust security solution with implemented SDP technology that caters to diverse scenarios, including segmented work networks and remote access for smart factories.